Hey! Lets Talk about your project
We’ll contact you within a couple of hours to schedule a meeting to discuss your goals.
What Is Encryption And How To Choose The Right One?
Posted on : 19 April, 2024
Have you ever wondered how your digital secrets are protected from cyber-attacks?
It is always the trusty "Encryption" that keeps all your personal information safe and secure. It refers to the process of converting or scrambling data and information into an unreadable, encoded format that may only be accessed by authorized individuals.
This blog provides you with a comprehensive overview of encryption. The advantages and disadvantages of encryption, how it works, the different types encryption for your needs.
What Is Encryption:Why Is It Important?
The encryption process serves as a fortified wall designed to safeguard your data from cyber threats. During this process, plaintext becomes ciphertext, an incomprehensible cipher that turns readable text into incomprehensible ciphertext.
Encryption works like a digital lock, so only those with the correct password can decode and access the data. The encryption of data makes sure sensitive information remains inaccessible to unauthorized parties, regardless of how your business generates, aggregates, or consumes data.
You can use encryption when,
- Secure Communications
- Protected Data Storage
- Safe Online Transactions
- Encrypted File Sharing
- Protection of Sensitive Documents
- Authentication Security
- Mobile Device Security
- Email confidential data
Different Types Of Encryption?
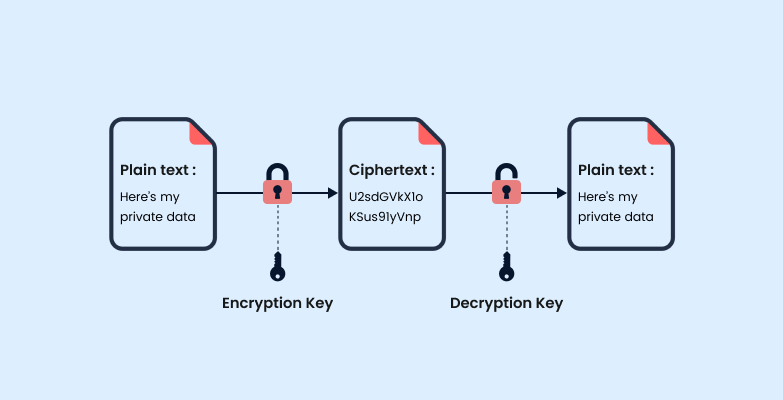
Symmetric Encryption?
Symmetric encryption has a single key that is used for encryption and decryption. A secure method must be considered to transfer the key between sender and recipient.
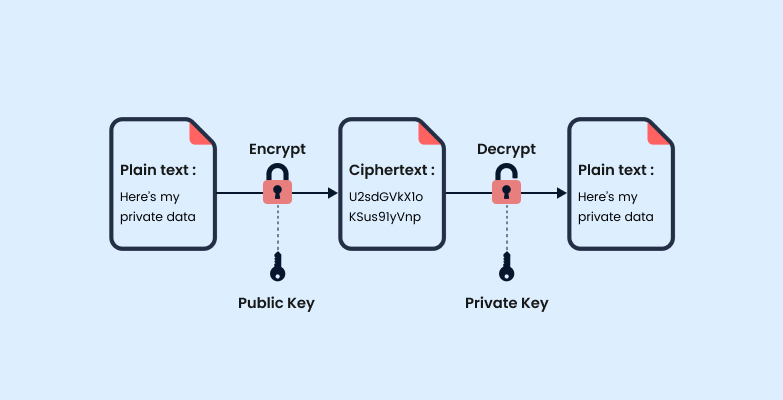
Asymmetric Encryption?
An asymmetric encryption process uses a pair of keys for encryption and decryption. One is called the private key, and the other is called the public key. The private key is exclusively used for decryption, while the public key is employed for encryption. The public key can be shared among authorized recipients or made available to the public for specific purposes.
Advantages And Disadvantages Of Encryption
Here we can discuss the advantages and disadvantages of encryption.
Advantages Of Encryptions
- Encryption helps secure and protect your data.
- This encryption encodes the information that only authorized parties can decipher it.
- Encryption safeguards against data breaches and unauthorized access.
- It helps safeguard individual privacy.
- It allows you to communicate and share information securely, which shields your personal and sensitive data.
- This helps organizations comply with regulations by providing mechanisms that secure data both in transit and at rest.
- It helps foster trust and confidence among users by assuring their data is secure.
- Encryption helps in sectors like finance, healthcare, and ecommerce.
- Even if a hacker gains access to encrypted data, they would not be able to use it without the encryption key.
Disadvantages Of Encryptions
- The user couldn't explore the encrypted file if the password or key got lost.
- Using simple keys in data encryption makes the data insecure and randomly accessed.
- Data encryption is an expensive technique, and the process can be time-consuming and resource-intensive. Encryption requires proper essential management practices, and the process can be complex.
- Encrypting and decrypting data can impose a performance overhead. This overhead can affect system responsiveness and throughput, especially in high-traffic scenarios.
How Does Encryption Work?
Step 1: Plaintext
You have a message or some information you want to keep secret. This is your starting point, called plaintext.
Step 2: Encryption Algorithm
You use a special lock called an encryption algorithm to scramble your message. This creates another version of your original message, which is now called a ciphertext.
Step 3: Key Generation
Next, you need a key like a secret code. The number of keys depends upon the type of encryption.
- Symmetric encryption: They use the same key for both encryption and decryption.
- Asymmetric encryption: It involves a pair of keys, one public and one private.
Step 4: Encrypting Message
In symmetric encryption -
- Using a symmetric key helps to both lock and unlock your message.
- You put your key into the lock along with your message, and it rearranges your message into ciphertext. In asymmetric encryption - There are two asymmetric keys: a public key and a private key. You use the recipient's public key to lock your message. It's like putting your message in a box that only they have the key to open.
Step 5: Transmission
You keep your locked-up message safe. If you're sending it to someone else, make sure it's sent securely so nobody else can get their hands on it.
Step 6: Decrypting the Message
- If it's symmetric encryption, they use the same key you used to lock it.
- If it's asymmetric encryption, they use their private key, which is like the special key that only they have.
Step 7: PlainText
Once the message is unlocked, it's back to its original form—your plaintext. Now, the recipient can read, use, or process the information as needed.
Conclusion
In conclusion, understanding encryption is beneficial for your privacy and security. In this blog, we have discussed the fundamentals of encryption and explored various types of encryption. So remember to consider factors such as the security needed, compatibility with your systems, and the implementation. Always choose the correct encryption method tailored to your specific needs. You can safeguard your sensitive information effectively with the proper encryption method. Encryption not only protects your data but also fosters trust among users.

































 Talk to our Expert
Talk to our Expert
